Below chart displays possible blood sugar levels (in fasting state). Units are expressed in mg/dL and mmol/L respectively.
Additional topics:
What is diabetes?
How do you know if you have diabetes?
How to test for diabetes?
Why is it important to measure your blood sugar levels frequently?
Diet for people with diabetes
You can also download or print this chart by clicking here.
Reference: American Diabetes Association, http://diabetes.org/
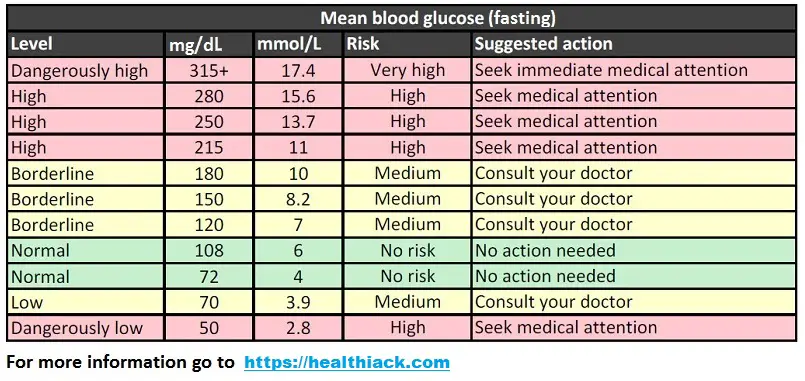
Fasting blood sugar levels chart
Additional topics:
What is diabetes?
How do you know if you have diabetes?
How to test for diabetes?
What is normal blood sugar level?
Why is it important to measure your blood sugar levels frequently?
Diet for people with diabetes
Blood Sugar 101
Definitions
Blood sugar, or blood glucose, is a source of energy that human body can process. Our body produces glucose by digesting the food we eat. It then goes through our intestines to the bloodstream and later in our muscles and other organs to be used as a fuel. In order for this mechanism to work, our pancreas has to be healthy to produce enough insulin.
If cells do not respond properly to the insulin levels this may result in a condition called insulin resistance and can lead to prediabetes and diabetes.
Blood Sugar Levels
Normal blood sugar levels are not higher than 100 mg/dL during the fasting period (at least 8 hours), or less than 140 mg/dL two hours after a meal. Blood sugar levels higher than this is considered hyperglycemia, while lower values are categorized as hypoglycemia.
Prolonged high values of blood sugar can lead to complications that can permanently damage the patient’s organs and tissues. The hormone in charge of maintaining our blood sugar on an optimum level is called insulin.
What is Insulin?
Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas, and its main purpose is to allow glucose to enter our cells. When we digest food and glucose enters our bloodstream, that is the signal for the pancreas to release insulin. Insulin then signals our cells to start using glucose as fuel. Excess glucose is being transformed into glucan and stored in the liver as glycogen.
During the starvation period, the pancreas releases glucagon, which elevates the levels of blood sugar by signaling the liver to transform glycogen back into glucose.
Signs and Symptoms of High and Low Blood Sugar Levels
The most frequent symptoms of hyperglycemia are:
• Frequent urination
• Thirst
• Headache
• Weakness
• Shortness of breath
• Nausea
• Vomiting
• Bad breath
• Dry mouth
• Stomach pain
Signs of low blood sugar levels include sweating, irregular heartbeat, shakiness, anxiety, nervousness, hunger, nausea, irritability, or confusion.
Risks of High/Low Blood Sugar
Some of the risks of hyperglycemia or high blood sugar levels include:
• Stroke
• Heart problems
• Kidney failure
• Vision impairment
• Weakened immune system
• Infections
• Poor circulation
• Nerve damage
• Problems with wound healing
Potential risks of prolonged low blood sugar are seizures, nerve damage, starvation, weakness, nervousness, and accidents due to person’s inability to react properly and on time.
Treatment
Getting your blood sugar levels back to normal requires certain lifestyle changes including regular workout, a diet based on proteins, fibers, and healthy fats. Also, it is recommended to have at least five small meals per day and make sure not to skip breakfast. If you suffer from diabetes, take your insulin and other medications as prescribed, and do not forget to monitor your blood glucose levels on a regular basis.
Overall
Blood sugar is actually glucose in our blood that our cells use for energy. We get it by digesting the food we eat. In order to be used as fuel, insulin has to be released into the bloodstream and signal cells to start using glucose.
If the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin or our body is getting resistant to it, it can lead to elevated levels of blood sugar. If prolonged, this condition can lead to severe health problems and even death. In order to keep glucose on an optimum level keep a healthy lifestyle, eat a balanced diet and exercise. If you have diabetes, take your meds as prescribed and measure blood sugar levels according to your schedule.
Reference: American Diabetes Association, http://diabetes.org/





































