A diabetes pump or an insulin pump, is a gadget designed for diabetic patients. Via a catheter, it delivers insulin into the body throughout the day.
The gadget is easy and convenient to carry around. It can be placed inside pockets, or clipped onto a belt, just as shown in the image below.
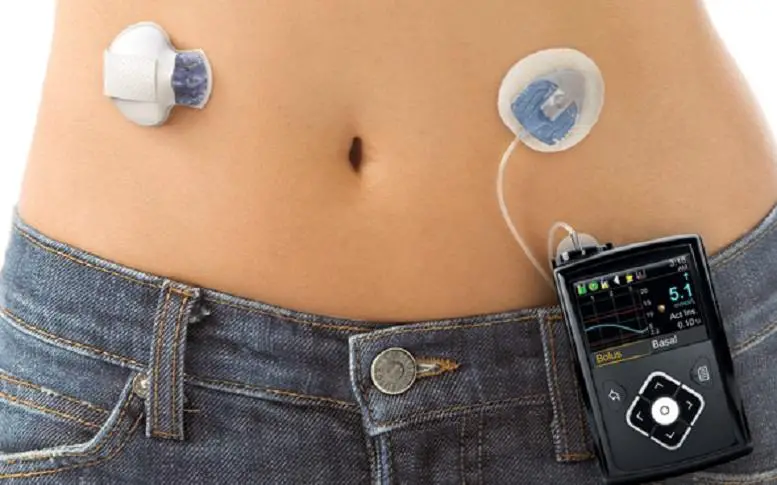
On this image: diabetes pump; image source: healthiack.com
Functions of an insulin pump
There are three main doses of insulin, which the insulin pump can deliver:
- Basal rate – the basal rate is a dose that is pumped non-stop throughout the day. It helps maintain the levels of blood glucose at a constant rate all through the night and in between meals.
- Bolus dose – the bolus dose is pumped as and when needed. This is done when there is a need to compensate for the presence of carbohydrates in a meal
- Supplemental/correction dose – the correction dose is needed when it is necessary to lower the levels of blood glucose that are currently high.
Benefits of an insulin pump
Some of the advantages of the diabetes pump include the following:
- Convenience – since the insulin pump delivers insulin automatically, or according to the personal settings, a user of a diabetes pump enjoys convenience since they don’t have to abide by a restrictive schedule with regards to daily activities, eating and so on.
- Less work – diabetic patients who have to inject insulin into their bodies intravenously can end up with an average of approximately 120 syringe injections every month. But with an insulin pump, on the other hand, the infusion set needs only to be changed an average of 12 times every month.
- More control – a insulin pump enables a user to have more control over their condition. This is because the pump is more accurate and precise than other methods of insulin regulation.
Being an easy-to-use gadget, a diabetes pump ensures your blood sugar levels are well regulated. This is necessary if the complications associated with diabetes such as those affecting the heart, eyes, nerves and kidneys are to be kept at bay.









































