Overview & Description
Electromyography (EMG) is used to test the electrical activity of a skeletal muscle.
Who is a candidate for the test?
An EMG is used to detect disorders that mainly affect the muscles. It is also used to diagnose muscle problems caused by other diseases, such as nerve dysfunction. An EMG can show the difference between true weakness and the reduced use of a muscle due to pain or lack of motivation. Peripheral nerve damage, known as peripheral neuropathy, can also be detected on an EMG.
How is the test performed?
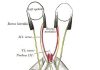
A needle electrode is placed into a skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones, and are the muscles that control posture and movement. The electrical activity of the muscle is displayed on an oscilloscope as an electrical waveform. An amplifier can be used so that the sound of the electrical activity can also be heard. During the test, the person may be asked to contract the muscle slowly. The test takes about 30 to 60 minutes. There may be some discomfort when the needle electrode is inserted.
Preparation & Expectations
What is involved in preparation for the test?
There is usually is no special preparation for an EMG. The doctor can provide any specific instructions.
Results and Values
What do the test results mean?
Disorders or conditions that cause abnormal results include:
Article type: xmedgeneral