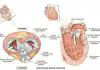
Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside of theuterus. The most common site is within a fallopian tube. More rarely an embryomay implant within an ovary, in the cervix, or on the abdominal wall.
What is going on in the body?
One out of every 200 pregnancies is ectopic. Although the fertilized egg is notcradled within the uterus, the embryo continues to grow and expand. Most ectopic pregnancies occur in a fallopian tube. Without treatment, the tubecan rupture. That can cause many serious problems and sometimes death.
What are the causes and risks of the condition?
Usually, an ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg is slowed or blockedin some way as it travels down the tube to the uterus. The stage may be set forthis by:
Symptoms & Signs
What are the signs and symptoms of the condition?
If a woman has an ectopic pregnancy, she may:
If the fallopian tube ruptures, a woman may:
Diagnosis & Tests
How is the condition diagnosed?
Tests that may be done to help diagnose an ectopic pregnancy include:
Prevention & Expectations
What can be done to prevent the condition?
Not every ectopic pregnancy can be prevented. However, a woman should avoidrisk factors that make ectopic pregnancy more likely to occur, including:
If a woman who has had a tubal ligation has a positive pregnancy test,she probably has an ectopic pregnancy. She needs further tests right away.
Four of out 10 ectopic pregnancies occur in women between 20 and 29 years old.Over 75% of these cases are diagnosed before the 12th week of pregnancy.
What are the long-term effects of the condition?
A woman’s symptoms will last and grow worse as long as the ectopic pregnancyexists. A rupture causes more pain and serious problems if not diagnosed andtreated. These problems can include:
When surgery is done to treat a ruptured ectopic pregnancy, a later, normalpregnancy is possible inabout half of the cases. In the other cases, infertility occurs.
What are the risks to others?
An ectopic pregnancy is not contagious. It poses risks only to the mother andthe fetus.
Treatment & Monitoring
What are the treatments for the condition?
Treating an ectopic pregnancy early can help prevent a rupture of the fallopiantubes and other serious side effects. Treatment options depend upon how soonthe diagnosis is made, whether or not rupture has occurred, and the location ofthe ectopic pregnancy.
A woman with a very early ectopic pregnancy that has not ruptured may be givenmethotrexate through a vein in her arm. This medication destroys the pregnancy.The woman would then be monitored closely in the hospital through blood testsand hormone level readings to make sure the pregnancy has ended.
Laparoscopy may be used todiagnose and treat an ectopic pregnancy if there is no tubal rupture oremergency. By using tiny instruments to remove the pregnancy, a surgeon may beable to preserve the affected tube. However, the embryo cannot be implanted afterwardsin the uterus to keep growing. This method requires a short overnight stay inthe hospital.
A woman needs emergency treatment if an ectopic pregnancy has ruptured and shehas signs of internal bleeding, such as shock, low blood pressure, and an enlarging, painful belly. Anexploratory laparotomy, which involves an incision in the abdomen, is doneright away. Her shock is treated with fluids given through a vein, bloodtransfusion, and medications to maintain blood pressure. Usually, blood clotshave to be removed along with the affected fallopian tube.
What are the side effects of the treatments?
Surgery may cause bleeding, infection, and allergic reaction to anesthesia.Side effects of methotrexate include kidney failure, blood disorders, and nervedamage.
What happens after treatment for the condition?
How long a woman must be hospitalized depends on the treatment and the amountof blood loss. A woman should use birth control for at least three months aftersurgery to let her body recover and allow tissues to heal. She may wish to havea follow-up test to see if her fallopian tubes are open or blocked.
How is the condition monitored?
Between 10% to 20% of women treated for an ectopic pregnancy will have anotherectopic pregnancy at a later date. If a woman who has had an ectopic pregnancymisses a period or notices symptoms of pregnancy, she should have a serum pregnancy test right away. If she is pregnant, she should getearly prenatal care and have a pregnancy ultrasound done to check the embryo’s location. Any newor worsening symptoms should be reported to the healthcare provider.
Article type: xmedgeneral