Overview & Description
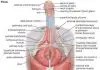
Colposcopy involves the use of a special lighted microscope to magnify thesurface of the cervix during a pelvicexamination. The cervix is the lowest part of the uterus andcontains the opening from the uterus to the vagina.
Who is a candidate for the procedure?
A colposcopy may be used in combination with a cervical biopsy to detect cancer of the cervix or precancerous changes knownas cervical dysplasia. Acervical biopsy is usually done after a woman has abnormal results from aPapsmear that is done as part of a pelvic examination. A Pap smear is a test in which the provideruses a small spatula and a brush to gently scrape cells from the woman’scervix. These cells are sent to a lab for testing. The Pap smear may showearly, abnormal, cancer-like changes in the cells of the cervix.
A woman should have a colposcopy, as well as a cervical biopsy, if the following conditions apply:
.
.
.
.
How is the procedure performed?
A colposcopy is done with the woman lying on her back with her feet instirrups. The healthcare provider places a speculum inside the woman’s vagina.This instrument helps enlarge the opening of the vagina, which allows theprovider to see the cervix and vaginal interior.
The healthcare provider uses the colposcope to magnify and examine the cervixand vagina. To make cells more visible under the colposcope, the provider putsa mild solution of vinegar on the area. Sometimes the healthcare provider also usesa solution of weak iodine.
If a cervical biopsy isbeing done at the same time as the colposcopy, the healthcare provider takes smallbits of tissue, or a biopsy, from suspicious areas. The technique is calledcervical punch biopsy. The woman may feel a brief pinch or cramp. Thehealthcare provider records the location of the abnormal areas and sends thetissue sample or samples to a lab to be viewed under a microscope.
Preparation & Expectations
What happens right after the procedure?
Cramping usually passes within minutes of the colposcopy. If she sits up tooquickly, a woman may feel lightheaded. Lying down for a few minutes after theprocedure prevents this. Any further cramping may be treated with anover-the-counter painmedication, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
If a biopsy was also done, the biopsy samples are sentto the laboratory to be examined under the microscope by the pathologist. Thehealthcare provider discusses the pathologist’s findings with the woman.Abnormalities can range from mild cervical dysplasia, or slightlyabnormal changes in the cells examined, to cancer of the cervix.Treatments and follow-up depend upon the exact diagnosis.
Home Care and Complications
What happens later at home?
For 1 to 2 days after a colposcopy and cervical biopsy, a woman may have asmall amount of pinkish discharge from the vagina. For 2 to 3 daysafterward, she should avoid sexual intercourse, douches, and tampon use.
What are the potential complications after the procedure?
A woman may experience minor bleeding after a colposcopy and cervical biopsy.Other potential complications include heavier vaginal bleeding, infection, orallergic reaction to theiodine used in the procedure. Any new or worsening symptoms should be reportedto the healthcare provider.
Article type: xmedgeneral