Overview & Description
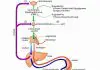
Magnetic resonance imaging, known as MRI, is a noninvasive imagingtechnique. It is used to view organs, soft tissue, bone, and other internalbody structures. In a cranial MRI, the person’s head is exposed to radiowaves while in a magnetic field. A cross-sectional picture of the skulland brain is produced by energy emitted from hydrogen atoms in thebody’s cells. The person is not exposed to radiation during this test.
Who is a candidate for the test?
A cranial MRI can be used for several reasons. It is themost sensitive type of exam to identify:
How is the test performed?
Before the test, the doctor will ask if the person:
A woman will also be asked if she might be pregnant.
As the test begins, the person lies on a flat platform. Theplatform then slides into a donut-shaped machine where the scanningtakes place. To help keep the final images clear, the person mustlie very still during the whole test.
A special substance called a contrast agent is oftengiven before or during the test. The contrast agent is used to enhanceinternal structures and improve image quality. Typically, this agent isinjected into a vein in the arm.
The scanning process is painless. However, the part of thebody being imaged may feel a bit warm. This feeling is harmless andis nothing to be concerned about. The person will hear loud bangingand knocking noises duringmany stages of the exam. Earplugs are provided for people who don’tlike the noises.
After the test, the person is asked to wait until the imagesare viewed to see if more pictures are needed. If they look OK,the person can leave.
Preparation & Expectations
What is involved in preparation for the test?
Before the test, the person is asked to remove all metalobjects that might affect imaging. These items include jewelry, hearingaids, hairpins, eyeglasses, and removable dental work. Also, theperson should inform the MRI technologist about any previoussurgery that required placement of metal, such as ahip pinning.Internal metal objects that cannot be removed may distort the final images.Since the magnetic field can damage watches and credit cards, theseobjects are not taken into the MRI scanner. Food and fluid do not needto be restricted before an MRI.
Results and Values
What do the test results mean?
A special doctor called a radiologist analyzes the MRI images.Cranial MRIs can reveal the size and location of tumors, blood vesselabnormalities, hemorrhages, and other soft-tissue problems. MRI isuseful in evaluating bony disorders that affect the skull. The person’sdoctor and the radiologist will use this information to help guide thenext course of action.
Article type: xmedgeneral