Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
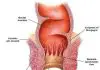
Atrophic vaginitis is an erosion of the vaginal tissues. This conditionusually occurs after a woman has gone through menopause.
What is going on in the body?
Low levels of estrogen cause a loss of lubrication, or moisture, in thevaginal tissues. At the same time, the vagina receives less blood supply and nutrients.And those two changes together can cause the vaginal wall to thin out. Women havelow levels of estrogen at certain times of life:
At these times, the vagina also becomes less acidic. Harmfulbacteria may replace the germs that are usually found in the vagina. So the vagina becomesmore prone to trauma and infection.
What are the causes and risks of the condition?
This condition occurs when the ovaries produce too little estrogen. It isvery rare in children. In women who have this condition, infection and trauma duringintercourse become more likely.
Symptoms & Signs
What are the signs and symptoms of the condition?
Some women have no symptoms. But many women report symptoms such as:
Diagnosis & Tests
How is the condition diagnosed?
A doctor will do a pelvic examto assess the health of the vaginal tissue. He or she can also check vaginal dischargefor signs of infection. Typical signs include large numbers of white blood cells andbacteria.
Prevention & Expectations
What can be done to prevent the condition?
Doctors may prescribe hormone replacement therapy, called HRT, toprevent and treat atrophic vaginitis. HRT usually consists of estrogen. A person can takeestrogen in several forms:
Some women may benefit from a diet high in foods that contain plantestrogens, known as phytoestrogens.These include soy, flaxseeds, and red clover.
What are the long-term effects of the condition?
Long-term effects of this condition include chronic Candida albicans,\ \
What are the risks to others?
Atrophic vaginitis itself is not catching. But, sometimes an infectiondevelops as a result of the condition. And this infection may be passed to a sexualpartner during intercourse.
Treatment & Monitoring
What are the treatments for the condition?
HRT is the treatment for low levels of estrogen in a woman’s body. Vaginalcreams used to treat this condition are usually applied two or three timesa week. Estrogen tablets may be given alone if the uterus has been removed.Otherwise, estrogen may be combined with progestin. Skin patches of estrogen maybe used instead of pills. The patches only need to be changed once or twice a week,so they can be more convenient to use.
A woman with this condition can also use these measures to help prevent irritation of the vagina.
What are the side effects of the treatments?
Estrogen creams can cause vaginal spotting. The cream itselfmay also be irritating. Estrogen pills and patches may cause the following side effects:
These side effects generally go away within a month or so after starting HRT, as the body adjusts.
What happens after treatment for the condition?
Without treatment, this condition and its symptoms will not go away.With treatment, symptoms will improve for as long as the treatment lasts. Normal vaginalmoisture usually returns after 2 to 4 weeks of vaginal cream therapy.
How is the condition monitored?
Once treatment has eliminated the symptoms, be sure to make follow-upvisits to the doctor. At least once a year, the doctor should do a pelvic examinationand physical. Report any new or worsening symptoms to the doctor.
Article type: xmedgeneral