Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
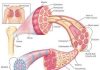
Intrinsic factor is a protein made by the stomach that helps thebody take in B1\ \
What is going on in the body?
In most people, the stomach makes the intrinsic factor protein. This protein attaches to the B1\ \
When children are born without the intrinsic factor protein, they developB1\ \
What are the causes and risks of the disease?
A congenital lack of intrinsic factor is thought to be inherited in most cases.
Symptoms & Signs
What are the signs and symptoms of the disease?
A child with a congenital lack of intrinsic factor usually develops normally during the first 6 to 12months of life. After this time, symptoms slowly begin and may include:
Diagnosis & Tests
How is the disease diagnosed?
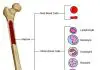
A congenital lack of intrinsic factor may be suspected after the history and physical exam. A bloodtest called a complete blood count, or CBC, is done first. This test counts the number of cells in the blood and will show a low number of red blood cells if anemia is present. Next, a blood test called a B1\ \
The diagnosis of congenital lack of intrinsic factor can be confirmed by a Schilling test, which uses radioactive vitamin B12 to measure the amount of B1\ \
Prevention & Expectations
What can be done to prevent the disease?
There are no known ways to prevent a congenital lack of intrinsic factor.
What are the long-term effects of the disease?
Most children have no long-term effects if the congenital lack of intrinsic factor is diagnosed andtreated promptly. If treatment is delayed, permanent damage to the nervoussystem may occur. This may include numbness, weakness, and cognitive impairments, or an impairedability to think logically. This damage may not go away with treatment.
What are the risks to others?
A congenital lack of intrinsic factor is not contagious. However, it is usually inherited. Genetic counseling may be helpful to couples with a family history of the disorder.
Treatment & Monitoring
What are the treatments for the disease?
Congenital lack of intrinsic factor is usually treated with injections of B1\ \
What are the side effects of the treatments?
Injections can cause soreness at the site of the needle stick.
What happens after treatment for the disease?
A person with congenital lack of intrinsic factor needs lifelong treatment. Most children grow up to be healthy and can lead normal lives with no restrictions. Further treatment may be needed if nervous system damage has occurred.
How is the disease monitored?
Monitoring is not usually needed unless nervous system damage is present. Any new or worsening symptoms should be reported to the healthcare provider.
Article type: xmedgeneral